1. Introduction
In today’s complex cybersecurity landscape, organizations face an escalating volume and sophistication of cyber threats. Traditional security approaches relying solely on manual incident response and rule-based detection methods are no longer sufficient to counter advanced persistent threats (APTs), sophisticated ransomware, insider threats, and zero-day exploits. To address these evolving challenges effectively, organizations worldwide require a strategic, integrated, and intelligent cybersecurity framework capable of automating threat detection, facilitating rapid response, and providing actionable intelligence.
SIEMLINE (Security Information Event Management Linked Intelligence and Network Enablement) is a comprehensive, globally applicable architecture framework specifically developed to enhance the capabilities of modern Security Operations Centers (SOCs) by integrating Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR), behavioural analytics, and advanced threat intelligence into a unified, interoperable architecture.
1.1 Purpose and Global Applicability
The SIEMLINE framework has been strategically designed to meet the stringent cybersecurity demands and compliance requirements of organizations operating across diverse geographic and regulatory landscapes, explicitly incorporating considerations relevant to:
- Australia: Including alignment with the Australian Cyber Security Centre’s (ACSC) Essential Eight, Australian Government Information Security Manual (ISM), Protective Security Policy Framework (PSPF), and Australian Privacy Act 1988.
- United States: Conforming with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), NIST Special Publications (800-53, 800-171, 800-207 for Zero Trust), Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), and regulatory compliance requirements including Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA).
- Europe: Adhering to standards and regulations including ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security Management), ISO/IEC 27701 (Privacy Information Management), ISO/IEC 42001 (Responsible AI Management), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), EU Network and Information Security (NIS/NIS2) Directive, and the forthcoming European Union AI Act.
By explicitly embedding these standards, SIEMLINE ensures that organizations achieve robust security posture, regulatory compliance, and operational resilience, while facilitating seamless cooperation across jurisdictions.
1.2 Why SIEMLINE?
SIEMLINE emerges as a timely solution addressing key limitations of traditional security models by integrating multiple cybersecurity capabilities into a cohesive framework. Its architecture prioritizes:
- Advanced Threat Detection: Combining signature-based, anomaly-based, and behavioural analysis methodologies to ensure threats are identified early, minimizing risk exposure.
- Security Automation and Orchestration: Streamlining security operations through automated workflows and orchestrated responses, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing the Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR).
- Real-Time Intelligence Integration: Incorporating structured and unstructured threat intelligence data from globally recognized sources, providing comprehensive situational awareness to proactively anticipate and neutralize threats.
- Enhanced Visibility and Control: Enabling unified visibility across network infrastructure, endpoints, cloud environments, and IoT ecosystems through centralized logging, analysis, and reporting mechanisms.
1.3 Integration with Global Cybersecurity Standards
Recognizing the criticality of regulatory compliance and interoperability, SIEMLINE integrates seamlessly with established global standards and frameworks, facilitating broad compliance and operational assurance:
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 (Information Security Management): Ensuring structured risk management, information protection, and continuous compliance through robust information security controls.
- ISO/IEC 27701 (Privacy Information Management): Complementing GDPR and Australian Privacy Act compliance through structured privacy and data protection measures, ensuring personal data security and management.
- ISO/IEC 42001 (Responsible AI Management): Embedding principles of ethical AI usage, transparency, accountability, and continuous risk management into the automated threat detection and response processes, ensuring trustworthy AI integration.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (USA): Aligning with the Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover methodology, providing comprehensive security life cycle management aligned to federal guidelines.
- ACSC Essential Eight (Australia): Direct alignment with maturity models, emphasizing controls like Application Control, Patch Management, Multi-Factor Authentication, and Privileged Access Management, crucial to Australian government and regulated industries.
- European Union’s GDPR and NIS2 Directives: Ensuring comprehensive cybersecurity incident reporting, data privacy, breach notification, and stringent data protection measures, enabling European and multinational organizations to achieve regulatory confidence and compliance.
1.4 Strategic Benefits for Organizations
Implementing SIEMLINE delivers multiple strategic advantages:
- Unified Governance: Enables a coherent and unified security governance approach across global business units and subsidiaries, streamlining compliance management.
- Reduced Complexity: Simplifies the deployment, integration, and management of cybersecurity tools and processes, minimizing complexity and enabling efficient use of resources.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Automates repetitive and manual tasks, freeing security teams to focus on strategic, high-impact cybersecurity initiatives.
- Improved Cyber Resilience: Proactive identification and management of threats enhance organizational resilience, minimizing downtime, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
- Global Regulatory Compliance: Facilitates effortless adherence to multiple global cybersecurity and privacy standards, significantly reducing compliance risk and operational overhead.
1.5 Architectural Principles of SIEMLINE
The SIEMLINE architecture framework is built upon the following foundational cybersecurity principles:
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Continuous verification, least-privilege access, and secure segmentation at every layer to ensure that trust is dynamically validated.
- Defense-in-Depth: Multiple security layers and redundancies across endpoints, networks, applications, and data repositories to maximize threat containment and mitigation.
- Context-Aware Intelligence: Leveraging sophisticated machine learning and deep learning models to provide actionable intelligence based on contextual insights and real-time threat analytics.
- Interoperability and Modularity: Supporting open standards and integration capabilities, enabling organizations to leverage best-of-breed tools and prevent vendor lock-in.
SIEMLINE is a sophisticated cybersecurity architecture framework designed to enable organizations globally to effectively navigate the complexities of the modern threat landscape. By aligning with prominent international standards and integrating intelligent cybersecurity solutions, SIEMLINE equips organizations to achieve robust security posture, regulatory compliance, and operational excellence. It represents not only a technological solution but also a strategic enabler, enhancing cyber resilience and ensuring responsible digital governance in a connected world.
2. Purpose and Scope
2.1 Purpose of SIEMLINE
The primary purpose of SIEMLINE (Security Information Event Management Linked Intelligence and Network Enablement) is to deliver an advanced, comprehensive cybersecurity architecture framework that addresses evolving cyber threats through an integrated approach combining Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR), and real-time behavioral threat intelligence. SIEMLINE addresses fundamental limitations of traditional SIEM solutions by embedding intelligence-driven analytics, automation, and response capabilities directly into security operations.
The overarching objectives of SIEMLINE are:
2.1.1 Enhanced Threat Detection and Prevention
- Employ advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time correlation to identify threats proactively.
- Provide integrated behavioural analysis, enabling detection of sophisticated attacks that bypass traditional detection methods.
- Utilize standardized threat intelligence frameworks (e.g., MITRE ATT&CK, OpenCTI, and STIX/TAXII) to improve accuracy, minimize false positives, and reduce analyst fatigue.
2.1.2 Automation and Operational Efficiency
- Automate routine incident response tasks, enhancing the speed, consistency, and effectiveness of security operations.
- Implement Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) principles, streamlining workflows, incident triage, and threat mitigation processes.
2.1.3 Real-Time Situational Awareness
- Integrate multiple sources of threat intelligence, providing comprehensive visibility into emerging threats.
- Enable proactive cybersecurity practices, such as threat hunting and predictive analytics, to detect potential threats before they materialize into impactful incidents.
2.1.3 Regulatory and Standards Compliance
- Support alignment with prominent cybersecurity frameworks and regulatory requirements, specifically tailored to:
- Australian frameworks: ACSC Essential Eight, PSPF, ISM, Australian Privacy Principles (APP).
- U.S. frameworks: NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), HIPAA, FISMA, CMMC, FedRAMP.
- European frameworks: GDPR, NIS2 Directive, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27701, and ISO/IEC 42001.
2.1.3 Scalability and Flexibility
- Leverage modular, containerized architecture for scalability across complex IT environments, including hybrid, multi-cloud, and on-premises deployments.
- Provide the flexibility to integrate with existing and future cybersecurity technologies, reducing vendor lock-in and increasing solution longevity.
2.1.3 Improved Decision-making and Strategic Insight
- Generate actionable intelligence through comprehensive, real-time visibility and analytics, enabling informed cybersecurity decision-making and strategic risk management.
- Employ contextual analytics to facilitate proactive threat hunting, security optimization, and predictive insights to anticipate and counter emerging cyber threats.
2.2 Scope of SIEMLINE Implementation
The SIEMLINE architecture framework defines a structured methodology for planning, designing, implementing, and operating integrated SIEM solutions. The scope of SIEMLINE encompasses the full lifecycle of modern SIEM deployments, explicitly including:
2.2.1 Functional Components
- Log Collection and Analysis:
- Ingestion and processing of security event data from multiple sources, including network devices, endpoints, cloud platforms, and IoT sensors.
- Threat Intelligence Integration:
- Aggregation and contextualization of external threat intelligence feeds for proactive threat detection and incident prevention.
- Incident Response and SOAR:
- Automation of incident response workflows, including the creation, escalation, and management of security incidents.
- Facilitation of active response measures (endpoint isolation, remediation automation).
- AI and Behavioural Analysis:
- Deployment of AI models for predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and behavioural threat hunting to detect advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Visualization and Reporting:
- Real-time, interactive dashboards and customizable reporting for monitoring security posture, compliance tracking, and executive reporting.
2.2.2 Integration and Interoperability
- Defined methodologies and APIs to integrate seamlessly with:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools
- Network Detection and Response (NDR) systems
- Cloud service providers (CSPs)
- Existing cybersecurity frameworks (ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 27701, ISO 42001, NIST CSF)
2.2.2 Deployment Models
- Modular architecture supporting both on-premises and cloud-native deployments.
- Containerized deployments (Docker/Kubernetes) enhancing agility, reliability, scalability, and ease of maintenance.
- High-availability and disaster recovery considerations for critical operational continuity.
2.2.3 Security and Compliance
- Comprehensive implementation of security protocols such as:
- TLS 1.3 and HTTPS encryption for all data communications.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) mechanisms across user and microservice interactions.
- Compliance with regulatory mandates including GDPR, Australian Privacy Act, and U.S. federal cybersecurity requirements.
2.3 Key Stakeholders and Users
The SIEMLINE framework is designed to support a diverse range of stakeholders, explicitly targeting:
- Security Analysts and SOC Teams:
- Enhanced incident handling capabilities, reduced alert fatigue, and improved productivity.
- Chief Information Security Officers (CISO) and Governance Bodies:
- Strategic visibility into security operations, risk posture, and compliance management.
- IT Infrastructure Teams:
- Efficient and secure integration with existing infrastructure and services.
- Compliance and Risk Management Officers:
- Simplified governance and automated compliance reporting aligned with international and national cybersecurity standards.
2.4 Strategic Alignment and Benefits
The SIEMLINE architecture explicitly aligns with global and national strategies, ensuring that organizations not only meet current cybersecurity challenges but anticipate future threats through continuous improvement:
- Scalable Security Operations: Scalable deployments accommodate evolving threats and organizational growth.
- Proactive Cybersecurity Posture: Enables proactive threat detection, minimizing incident dwell time and risk exposure.
- Global Compliance Alignment: Directly supports international collaboration through harmonization with global standards, positioning organizations as leaders in cybersecurity best practices.
The SIEMLINE architecture framework establishes a comprehensive blueprint for implementing integrated, intelligent, and highly automated cybersecurity operations. By prioritizing proactive threat detection, response automation, and compliance alignment, SIEMLINE delivers strategic value that transcends geographic boundaries, empowering organizations in Australia, the United States, Europe, and globally to achieve cybersecurity excellence.
Through this structured approach, organizations can enhance their security posture, streamline operations, and position themselves confidently against evolving cyber threats, regulatory pressures, and operational complexities inherent in today’s digital landscape.
3. Core Components of SIEMLINE
The SIEMLINE architecture comprises interconnected core components designed to deliver a fully integrated, comprehensive Security Information and Event Management solution. These components provide seamless interoperability, modular scalability, and support for industry-standard cybersecurity frameworks, creating a robust security operations ecosystem. Each component aligns strategically with global cybersecurity standards, ensuring organizations across Australia, the United States, Europe, and beyond can effectively address sophisticated cyber threats.
The core components of SIEMLINE include:
3.1 Frontend Interface Layer
This layer provides an interactive, intuitive user interface that enables SOC analysts, security managers, and incident responders to visualize, investigate, and respond to security incidents effectively.
3.1.1 User Interface (UI)
- Interactive Dashboards:
- Built with modern front-end frameworks such as React.js or Angular, ensuring responsiveness, real-time data visualization, and customizable widgets.
- Delivers visual analytics on real-time threats, performance metrics, and compliance statuses.
- Advanced Query Capabilities:
- Facilitates real-time data exploration and threat hunting.
- Enables drill-down features into detailed threat data and contextual information.
- Incident Workflow Management:
- Seamless integration of SOAR capabilities, allowing SOC teams to initiate automated response actions directly from the UI.
3.1.2 Conversational AI Assistant (Chatbot)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)-Driven Assistance:
- Allows security teams to query data, trigger automated responses, and manage alerts through intuitive interactions.
- Accelerates incident analysis and improves efficiency through intelligent contextual assistance.
3.2 Backend Infrastructure and Microservices
SIEMLINE leverages a modular microservices architecture designed to ensure high performance, scalability, resilience, and ease of management.
3.2.1 API Gateway
- Provides secure routing, authentication (JWT/OAuth 2.0), rate limiting, and caching mechanisms.
- Manages communications securely between frontend and backend services.
3.2.2 Microservices Layer
The microservices architecture includes multiple independently deployable and scalable services, each addressing specific functionalities:
- Log Ingestion and Normalization:
- Collects and normalizes structured and unstructured log data from endpoints, network devices, cloud services, and applications.
- Threat Detection Service:
- Implements advanced rule-based and machine learning-driven threat detection using open standards (e.g., Sigma rules).
- Detects threats through behavioral analysis, anomaly detection, and correlation algorithms.
3.2.3 AI-Driven Analytics Service
- Deploys AI and machine learning models (e.g., TensorFlow/PyTorch) for predictive threat detection, anomaly detection, and behavior profiling.
- Continuously improves detection capabilities through adaptive learning and feedback loops.
3.2.4 Incident Response Automation (SOAR) Service
- Automates the incident response lifecycle with pre-defined playbooks and customizable response workflows.
- Supports integration with ticketing systems like Jira or ServiceNow, automating escalation and documentation.
3.2.4 Forensic and Investigation Services
- Provides forensic artifact collection, analysis, and response (leveraging tools like Velociraptor).
- Enables rapid identification of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) through endpoint and network data analysis.
3.3 Data Layer
Ensures robust storage, retrieval, and analytics of data collected from diverse sources, underpinning SIEMLINE’s threat detection capabilities.
3.3.1 Log Management
- Centralized log collection and management system leveraging Elasticsearch, Graylog, or similar platforms.
- Structured and unstructured log data aggregation, indexing, and query optimization for rapid retrieval and analysis.
3.2.5 Threat Intelligence Repository
- Integration with globally recognized threat intelligence platforms (OpenCTI, MISP).
- Real-time ingestion, correlation, and enrichment of data using standardized formats (STIX/TAXII).
3.2.6 Data Storage and Management
- Elasticsearch: Scalable real-time storage for log data, event analytics, and historical data retrieval.
- PostgreSQL: Manages structured relational metadata, configuration, and incident records.
- Redis/RabbitMQ: Facilitates caching, session management, and inter-service messaging.
3.3 Integration & Interoperability Layer
SIEMLINE emphasizes interoperability, providing integration capabilities across diverse cybersecurity and IT environments.
3.3.1 Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Standardized integration points supporting leading EDR tools for comprehensive endpoint visibility and response automation.
3.3.2 Network Detection and Response (NDR)
- Direct integration with NDR platforms, enabling advanced network threat detection through deep packet inspection (DPI) and flow analysis.
3.3.2 Cloud & Hybrid Environment Integration
- Extensive support for AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and private cloud environments for cohesive security visibility and monitoring.
3.4 Automation & Orchestration (SOAR) Layer
The SOAR capability automates and orchestrates incident response, significantly enhancing operational efficiency.
3.4.1 Playbook Automation
- Automates incident response procedures such as threat containment, isolation, remediation, and reporting.
- Enables pre-configured or custom playbooks based on standards such as MITRE ATT&CK techniques and NIST incident response frameworks.
3.4.2 Task Scheduling and Workflow Management
- Leverages messaging queues (RabbitMQ) and orchestration tools (Ansible, custom scripting) to automate security operations tasks reliably and consistently.
3.5 Security and Compliance Layer
This layer ensures compliance with global cybersecurity standards, regulatory requirements, and robust operational security.
3.5.1 Authentication and Authorization
- Employs JWT-based authentication and strict Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for microservices and API endpoints.
- Ensures auditability of actions and traceability of system interactions.
3.5.2 Data Security
- Implements encryption standards (AES-256 for data at rest, TLS 1.3 for data in transit).
- Ensures compliance with standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 27701, GDPR, and Australian Privacy Principles.
3.6 Monitoring & Reporting Layer
3.6.1 Observability and Performance Management
- Employs Prometheus and Grafana for real-time monitoring, providing system health metrics, resource utilization, and alert performance analytics.
3.6.2 Reporting and Compliance Dashboards
- Provides customizable reporting tools enabling compliance reporting aligned to global cybersecurity standards, facilitating audits and continuous improvement processes.
3.7 Scalability and Resilience Layer
3.7.1 Containerization & Orchestration
- Docker and Kubernetes-based deployments for maximum scalability, availability, and resilience across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
3.6.2 High Availability and Disaster Recovery
- Built-in redundancy and load balancing (NGINX, HAProxy) ensure continuity and minimal downtime during disruptions.
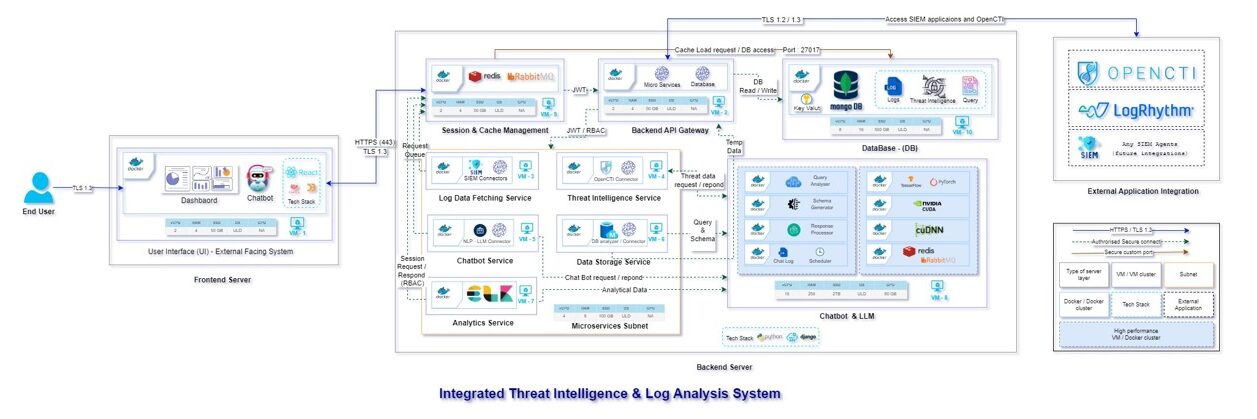
Below is an example of a fully-worked SIEMLINE architecture:
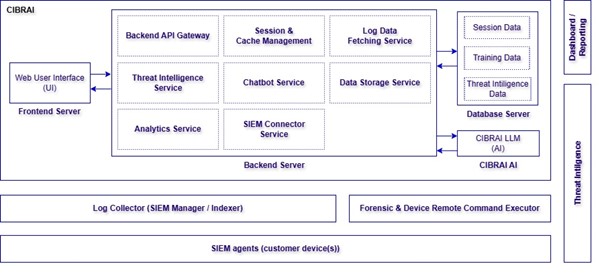
Figure 1. Logical architecture example using SIEMLINE architecture.
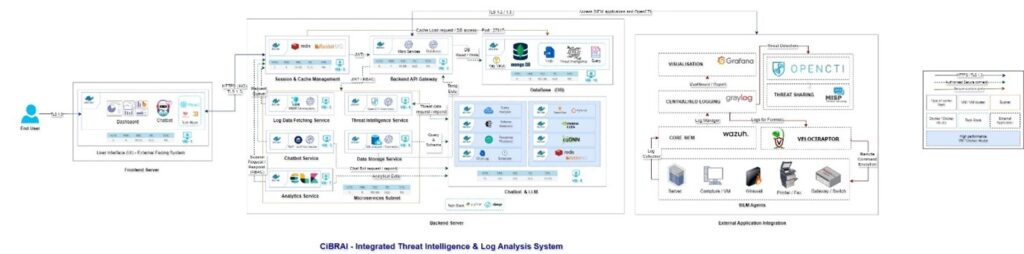
Figure 2. Example technical SIEMLINE deployment
The SIEMLINE framework’s core components collectively form a robust, comprehensive, and scalable cybersecurity architecture capable of managing and mitigating the dynamic threat landscape faced by modern enterprises and government agencies. By leveraging interoperability, automation, advanced analytics, and compliance management, SIEMLINE provides a globally applicable solution for enterprises and governments to proactively secure their environments, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain compliance across Australia, the United States, Europe, and beyond.
4. Deployment Strategy
The SIEMLINE architecture framework outlines a structured, robust, and globally scalable deployment strategy, designed to deliver secure, efficient, and continuously compliant cybersecurity operations. The deployment strategy leverages industry-leading practices in cybersecurity, infrastructure management, automation, and regulatory compliance to ensure SIEMLINE integrates seamlessly into diverse organizational and technological landscapes.
This strategic approach incorporates standards and regulations across key jurisdictions, notably Australia, the United States, and Europe, to guarantee comprehensive security, efficiency, and governance.
4.1 Containerization and Infrastructure Management
Leveraging modern containerization technologies ensures the flexibility, modularity, and scalability essential for modern cybersecurity deployments.
3.1.1 Containerized Deployments
- Docker:
- Facilitates rapid and standardized deployment of SIEMLINE components, ensuring consistency across development, testing, and production environments.
- Kubernetes:
- Provides robust orchestration, high availability, auto-scaling, and efficient management of SIEMLINE microservices, delivering exceptional operational resilience and continuity.
4.1.2 Infrastructure Automation
- Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform and Ansible streamline provisioning, configuration, and continuous management, reducing manual effort, minimizing errors, and ensuring compliance with cybersecurity standards.
4.2 Deployment Phases
The deployment strategy of SIEMLINE follows a phased approach to ensure structured implementation, continuous validation, and optimization across the entire lifecycle:
4.2.1 Phase 1 – Core Infrastructure and Log Management
- Establish the foundational infrastructure including backend services, Elasticsearch clusters, and initial log collection services.
- Integration of essential log collectors and parsers (e.g., syslog, journald, Windows Event Logs) for comprehensive data ingestion from endpoint, cloud, and network devices.
- Validate initial data ingestion, normalization, and indexing processes.
4.2.2 Phase 2 – Threat Intelligence and Behavioural Analytics
- Integrate threat intelligence platforms (MISP, OpenCTI) to enrich data for advanced threat detection.
- Deploy machine learning and AI-driven behavioural analytics engines (leveraging TensorFlow, PyTorch) to identify and analyse anomalous activities proactively.
- Validate the detection capabilities through initial threat simulation exercises and system tuning.
4.2.3 Phase 3 – Automation, Orchestration, and Incident Response
- Implement Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) capabilities to automate incident management processes.
- Deploy predefined security playbooks based on the MITRE ATT&CK framework to standardize and automate incident response activities.
- Integration with external incident management platforms such as ServiceNow SecOps, Jira, or TheHive for automated case management.
4.2.4 Phase 3 – Advanced AI Integration
- Implement advanced predictive analytics capabilities using AI models to anticipate potential security threats and enable proactive threat hunting.
- Enhance the interactive user interface with AI-driven recommendations, guided workflows, and automated contextual insights.
- Validate AI functionalities in real-world scenarios to ensure operational readiness, accuracy, and reliability.
4.2.5 Phase 4 – Continuous Enhancement and Optimization
- Establish continuous improvement processes based on regular audits, feedback, and evolving cybersecurity threats.
- Continuously expand integration with emerging cybersecurity technologies and frameworks.
- Conduct periodic scalability assessments and performance optimization to support evolving business needs.
4.3 Security and Compliance Management
Ensuring continuous compliance with global cybersecurity standards is a key feature of the SIEMLINE deployment strategy, with explicit alignment to regional standards including ACSC Essential Eight, NIST CSF, ISO 27001, GDPR, and NIS2 Directive.
4.3.1 Secure Communication and Data Protection
- Enforce TLS 1.3, HTTPS, and secure API communication channels across all system interactions.
- Implement data encryption for sensitive information both in-transit and at-rest.
- Regularly validate compliance with standards such as ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27701, GDPR, ACSC Essential Eight, and NIST guidelines.
4.3.2 Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Clearly defined and auditable access roles and permissions, reducing internal risk exposure.
- Maintain audit trails for user actions, ensuring accountability and traceability.
4.3.3 Auditing and Continuous Monitoring
- Schedule regular internal and external audits to assess and validate system performance, security controls, and compliance posture.
- Utilize continuous monitoring tools (Prometheus, Grafana, ELK stack) to ensure ongoing operational effectiveness and compliance adherence.
4.4 Automation and CI/CD Integration
Automation is central to SIEMLINE deployment, ensuring reliability, consistency, and agility.
4.4.1 Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
- Establish automated pipelines using tools such as Jenkins or GitHub Actions to streamline testing, deployment, and updating of SIEMLINE components.
- Automate security tests, penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security assessments as integral parts of the CI/CD pipeline to maintain a high-security posture.
4.4.2 Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Utilize IaC practices with tools such as Terraform or Ansible to automate provisioning, configuration, and ongoing maintenance of the SIEMLINE environment.
- Ensure version-controlled, repeatable infrastructure deployments to minimize configuration drift and operational errors.
4.5 Scalability and Disaster Recovery
SIEMLINE supports organizational growth and resilience through integrated scalability and disaster recovery strategies.
4.5.1 High Availability
- Deploy load balancing (NGINX, HAProxy) and multi-region redundancy to ensure high availability.
- Implement automated failover and disaster recovery procedures for minimal downtime.
4.4.3 Scalability and Performance
- Optimize SIEMLINE microservices and data storage solutions for horizontal and vertical scalability.
- Continuously monitor and adjust infrastructure using real-time insights from monitoring tools to ensure optimal performance under varying operational demands.
4.5 Training and Capability Development
The effectiveness of SIEMLINE depends heavily on the expertise of its operators and administrators.
4.5.1 Training and Capacity Building
- Deliver structured training programs for cybersecurity teams focused on SIEMLINE operations, threat detection methodologies, and incident response workflows.
- Provide continuous education on evolving cyber threats, SIEM technologies, and compliance standards relevant to each region.
4.5.2 Competency Assessments
- Regularly assess and update training programs to reflect evolving cybersecurity practices and technologies.
- Ensure staff remain skilled and knowledgeable in managing SIEMLINE components, incident handling, and regulatory compliance.
4.5 Harmonization with Global Standards and Compliance
SIEMLINE strategically integrates with internationally recognized cybersecurity frameworks to ensure global interoperability and compliance:
- Australia: ACSC Essential Eight, Australian ISM, PSPF.
- United States: NIST Cybersecurity Framework, FedRAMP, FISMA, HIPAA.
- Europe: GDPR, NIS2 Directive, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27701.
By aligning deployment strategies with these standards, SIEMLINE enables global organizations to achieve cybersecurity excellence, operational resilience, and regulatory compliance. The SIEMLINE deployment strategy is meticulously designed to provide global scalability, operational reliability, and compliance with international standards. Its structured and phased implementation, integrated automation, and continuous improvement mechanisms allow organizations to maximize the effectiveness and agility of cybersecurity operations. Through clear integration points, seamless interoperability, and automated lifecycle management, SIEMLINE positions itself as a leading cybersecurity framework, adaptable across diverse environments, and robust against evolving threats worldwide.
5. Recommended Technology Stack
The SIEMLINE framework advocates a modular, interoperable, and flexible technology stack designed to maximize security posture, scalability, and operational efficiency while adhering to international cybersecurity standards and best practices. This recommended technology stack provides a clear roadmap for selecting and deploying components capable of meeting the cybersecurity, governance, risk management, and compliance requirements in diverse global environments—including Australia, the United States, and Europe.
The technologies suggested are open, widely supported, and proven to deliver optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility without imposing vendor lock-in.
5.1 Frontend Technologies
User Interface (UI) and Visualization
- React.js (17.0+) / Angular (latest stable release):
- Highly responsive, interactive, and customizable interfaces.
- Enables seamless integration with backend APIs and microservices.
- Tailwind CSS / Bootstrap:
- Provides responsive, accessible, and visually consistent design.
5.2 Backend Technologies
API Gateway and Microservices
- Node.js (Express.js):
- Efficient and scalable API management and routing.
- Python (FastAPI / Django):
- Robust microservice development, AI integration, and backend logic.
- Redis (latest stable version):
- High-performance caching, session management, and in-memory data storage.
Messaging and Task Queuing
- RabbitMQ / Apache Kafka:
- High-performance messaging, event streaming, and task orchestration among microservices.
5.3 Data Management Layer
Log Collection and Analysis
- Elasticsearch (ELK Stack):
- Highly scalable real-time log analysis, indexing, and search functionality.
- Extensive visualization and analytics with Kibana.
- Graylog (optional alternative):
- Advanced log management, indexing, and correlation capabilities.
Relational Databases
- PostgreSQL:
- Robust, scalable database for structured metadata, configurations, and compliance records.
Time-Series Databases
- InfluxDB:
- Efficient storage, querying, and visualization of time-series metrics, critical for monitoring infrastructure health and performance.
- MongoDB:
- Flexible document-based database storage for threat intelligence, forensic analysis results, user interactions, and unstructured data.
5.4 Threat Intelligence and Forensics
Threat Intelligence Platforms
- OpenCTI / MISP (Open-Source Threat Intelligence Platforms):
- Real-time ingestion and correlation of threat intelligence using standardized protocols (STIX/TAXII).
- Mapping threat data against MITRE ATT&CK to enhance incident detection and response efficacy.
Forensic Analysis
- Velociraptor / Osquery:
- Endpoint forensic tools for artifact analysis and detailed endpoint telemetry to support proactive threat hunting and response.
5.5 Security Orchestration and Automation (SOAR)
Automation and Orchestration
- TheHive / Shuffle:
- Incident response orchestration, customizable playbooks, task automation, and integrations with leading incident management platforms such as ServiceNow, Jira, and Splunk Phantom.
- Ansible / Custom Python Scripts:
- Task automation, infrastructure management, incident mitigation workflows, and security policy enforcement.
5.6 AI and Machine Learning Technologies
Behavioural Analytics and Threat Detection
- TensorFlow (Deep Learning) / PyTorch (Neural Networks):
- Robust frameworks for building, deploying, and maintaining predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and behavioral analytics engines.
- Custom LLM and NLP Models:
- Enables intelligent alert enrichment, real-time contextual insights, and improved response accuracy through natural language queries and analysis.
- GPU Acceleration Libraries (NVIDIA CUDA, cuDNN):
- High-performance processing of large-scale AI workloads and model training.
5.7 Monitoring and Visualization
System Monitoring and Observability
- Prometheus / Grafana:
- Comprehensive monitoring, alerting, and visualization tools, delivering insights into infrastructure performance, security analytics, and operational metrics.
- ELK Stack (Kibana):
- Advanced visualization and reporting for comprehensive security dashboards, incident analysis, and real-time alert management.
5.8 Containerization and Infrastructure
Containerization and Orchestration
- Docker:
- Lightweight, standardized packaging of applications, simplifying deployment, updates, and scalability.
- Kubernetes (Orchestration):
- Automated management of deployments, scaling, and high availability, ensuring reliability and consistency.
5.8 Security and Compliance Technologies
Encryption and Communication Security
- TLS 1.3, HTTPS (Let’s Encrypt or Enterprise CA):
- Secure communication protocols for data protection in transit.
Authentication and Authorization
- JSON Web Tokens (JWT) / OAuth 2.0:
- Robust authentication and authorization standards for secure API access and microservices interactions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Fine-grained access management, compliant with regulatory requirements (GDPR, HIPAA, NIST, ISO standards).
5.9 Infrastructure Automation and CI/CD
Deployment Automation
- Jenkins / GitHub Actions (CI/CD Pipelines):
- Automated, repeatable build and deployment processes, reducing manual intervention and errors.
- Terraform / Ansible (Infrastructure as Code):
- Automated infrastructure provisioning and configuration management, ensuring reproducible and secure environments across global deployments.
5.10 Cross-Platform Compatibility and Integration
Standard Integration Frameworks
- REST APIs / gRPC APIs:
- Open APIs enabling smooth interoperability with third-party cybersecurity solutions and IT systems.
- Standardized Data Formats (JSON, XML, STIX/TAXII):
- Ensures seamless data interchange, analytics compatibility, and global threat intelligence sharing.
Summary
| Functional Area | Recommended Technologies |
| Frontend UI | React.js, Angular, Tailwind CSS, Bootstrap |
| Backend API & Microservices | Node.js (Express.js), Python (FastAPI/Django), Redis, RabbitMQ, Redis |
| Data Collection & Analysis | ELK Stack, Elasticsearch, Graylog, MongoDB, InfluxDB |
| Threat Intelligence & Forensics | OpenCTI, MISP, Velociraptor, Osquery |
| Automation & Orchestration (SOAR) | Playbooks, Ansible, TheHive, Custom scripting |
| AI & Machine Learning | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Custom AI Models |
| Monitoring & Visualization | Grafana, Prometheus, Kibana (ELK) |
| Security & Compliance | TLS 1.3, HTTPS, JWT/OAuth, RBAC |
| Containerization & Deployment | Docker, Kubernetes |
| Infrastructure Automation & CI/CD | Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Terraform, Ansible |
By aligning with this recommended technology stack, organizations adopting SIEMLINE can achieve a robust, scalable, secure, and globally compliant cybersecurity solution. This selection emphasizes operational excellence, proactive threat management, streamlined automation, and continuous compliance, positioning organizations to confidently address contemporary cybersecurity challenges while maintaining agility, flexibility, and resilience in an evolving digital threat landscape.
6. Benefits of SIEMLINE Architecture
The SIEMLINE (Security Information Event Management Linked Intelligence & Network Enablement) architecture framework is meticulously crafted to deliver tangible and strategic cybersecurity benefits, offering a comprehensive, integrated solution for organizations operating globally. By embedding advanced analytics, intelligence-driven security, automated orchestration, and compliance alignment, SIEMLINE positions organizations to effectively manage cybersecurity risks, improve operational efficiency, and achieve continuous compliance across diverse regulatory landscapes.
The following sections outline the extensive strategic and operational benefits that organizations will realize upon adopting the SIEMLINE framework:
6.1 Enhanced Threat Detection and Response
6.1.1 Advanced Analytics & Behavioural Detection
- Implements sophisticated analytics combining traditional SIEM methods with advanced machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), enabling rapid detection of complex threats including Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), insider threats, and zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Provides context-aware threat detection based on real-time behavior analysis, significantly reducing false positives and enhancing precision.
6.1.2 Proactive Threat Intelligence
- Integrates threat intelligence frameworks (e.g., MITRE ATT&CK, OpenCTI, MISP) allowing real-time contextual threat enrichment and predictive threat modeling.
- Proactively identifies potential threats through predictive analytics, empowering organizations to adopt preventative measures ahead of breaches.
6.1.3 Reduced Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR)
- Automates incident detection and response workflows using Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR), significantly reducing incident dwell time.
- Enhances operational agility, enabling rapid containment and remediation, minimizing threat impact on operations and assets.
6.2 Enhanced Operational Efficiency
6.2.1 Security Automation and Orchestration
- Automates repetitive and manual tasks, freeing security analysts to concentrate on complex investigative and strategic tasks.
- Streamlines operational workflows and reduces human error through standardized automated playbooks and procedures.
6.2.2 Integrated Incident Management
- Seamlessly integrates with existing incident management platforms (e.g., ServiceNow, Jira, Splunk), ensuring cohesive operational alignment and rapid escalation or resolution of incidents.
6.3 Improved Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC)
6.3.1 Continuous Compliance Alignment
- Direct alignment with international cybersecurity frameworks such as:
- Australia: ACSC Essential Eight, Australian Government ISM, PSPF, Privacy Act 1988.
- United States: NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), FedRAMP, FISMA, HIPAA.
- Europe: ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, NIS2 Directive, ISO/IEC 27701, ISO/IEC 42001.
- Facilitates automated compliance monitoring, reporting, and auditing, significantly reducing manual compliance efforts and ensuring continuous compliance and transparency.
6.2.3 Improved Auditability and Transparency
- Provides robust audit trails and logging capabilities, simplifying compliance auditing and enhancing organizational accountability and transparency.
- Real-time compliance dashboards facilitate monitoring and reporting aligned with regulatory expectations and industry standards.
6.3 Operational Scalability and Flexibility
6.3.1 Modular and Interoperable Design
- SIEMLINE’s microservices-based architecture allows for independent scaling and deployment of components, accommodating growth and evolving organizational needs effortlessly.
- Flexibly integrates with legacy systems and modern cybersecurity technologies, reducing vendor lock-in and ensuring long-term adaptability.
6.3.2 Cloud-native and Hybrid Deployment
- Offers seamless deployment capabilities across hybrid, cloud-native, or multi-cloud environments (AWS, Azure, GCP), ensuring flexibility and reducing operational complexity across geographically dispersed infrastructures.
6.4 Enhanced Security Posture
6.4.1 Proactive Risk Mitigation
- Enables proactive cybersecurity management through comprehensive, real-time visibility into threats across endpoint, network, and cloud environments.
- Empowers organizations with the tools required to identify and respond to potential vulnerabilities before exploitation occurs, reducing the overall attack surface and risk exposure.
6.4.2 Zero Trust Integration
- Aligns closely with Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA/ZTA) concepts, facilitating continuous verification, dynamic trust evaluation, and least-privilege access across all components, reducing attack surface and lateral movement risks.
6.5 Strategic Alignment with International Standards
6.5.1 Global Compliance Assurance
- SIEMLINE’s built-in alignment with international cybersecurity standards ensures compliance with multiple regional frameworks simultaneously, significantly reducing regulatory overhead and compliance complexity.
- Ensures consistency of cybersecurity practices across global business units, simplifying audits and enhancing governance effectiveness.
6.5.2 International Collaboration and Interoperability
- Facilitates global interoperability, collaboration, and information sharing through the adoption of widely recognized standards (ISO, NIST, ACSC), enhancing cross-border cybersecurity cooperation.
6.6 Enhanced Decision-making and Strategic Insight
6.6.1 Contextual and Actionable Intelligence
- Delivers real-time, context-rich insights derived from integrated threat intelligence and advanced analytics, empowering cybersecurity leaders to make informed, strategic decisions.
- Enhances executive reporting through comprehensive dashboards, trend analysis, and predictive modeling capabilities.
6.6.2 Strategic Cybersecurity Management
- Supports strategic security governance and risk management practices by providing real-time visibility into threat landscapes, operational efficiencies, and compliance maturity.
- Facilitates proactive cybersecurity strategy alignment, ensuring ongoing adaptation to emerging threats and technological advancements.
6.6 Resource Optimization and Cost Efficiency
6.6.1 Reduced Operational Overhead
- Automation of repetitive and manual security operations tasks reduces staffing costs and operational overhead, allowing optimized allocation of cybersecurity resources.
- Scalable architecture reduces the necessity for frequent costly infrastructure upgrades, ensuring cost-effective operation and scalability.
6.7 Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
6.7.1 Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
- Integration of continuous improvement methodologies (Plan-Do-Check-Act cycles) supports constant evolution of cybersecurity practices, keeping pace with emerging threats and regulatory changes.
- Supports continuous compliance frameworks (ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001), embedding ongoing enhancement into security operations.
6.6 Key Stakeholder Benefits Summary
| Stakeholder Group | SIEMLINE Benefits |
| Security Operations Teams | Enhanced detection, automated response, reduced fatigue |
| Chief Information Security Officers | Improved visibility, compliance alignment, strategic insight |
| IT Infrastructure Teams | Easy integration, simplified scalability, flexible deployments |
| Governance and Compliance Officers | Simplified compliance, automated reporting, reduced regulatory risk |
| Executives and Decision-Makers | Strategic insights, improved risk management, enhanced security posture |
The SIEMLINE architecture framework provides significant strategic, operational, and compliance-related benefits, equipping organizations globally with a comprehensive and proactive cybersecurity solution. Its robust integration capabilities, advanced analytics, and strategic alignment with international standards ensure enhanced cybersecurity posture, improved operational efficiency, and strengthened compliance management, positioning organizations to confidently address today’s complex cybersecurity landscape and future threats.
7. Conclusion
The SIEMLINE (Security Information Event Management Linked Intelligence & Network Enablement) framework represents a transformative evolution in cybersecurity architecture, designed specifically to equip organizations with the strategic, operational, and technical capabilities required to navigate today’s complex and dynamic global cybersecurity landscape. As threats continue to grow in sophistication and scale, organizations across the globe—particularly in Australia, the United States, Europe, and beyond—face significant pressures to maintain robust cybersecurity measures while complying with increasingly stringent regulatory frameworks.
SIEMLINE addresses these challenges directly, integrating advanced threat detection, proactive intelligence, robust automation, orchestration capabilities, and comprehensive compliance alignment into a single, cohesive architecture. This holistic framework enables organizations to shift from reactive security models toward a proactive, intelligence-driven approach, significantly improving cybersecurity resilience, operational efficiency, and strategic decision-making capabilities.
7.1 Strategic Advantages of SIEMLINE
The deployment of SIEMLINE offers organizations several distinct strategic advantages:
- Enhanced Security Posture:
- Employing AI-driven analytics and real-time threat intelligence for early detection and response to complex threats, significantly reducing exposure and minimizing damage.
- Operational Excellence and Efficiency:
- Streamlining security operations through extensive automation, freeing human analysts for critical, strategic tasks and reducing mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR).
- Robust Global Compliance:
- Seamlessly aligning with multiple international and regional cybersecurity and privacy frameworks such as the ACSC Essential Eight, ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and ISO standards (ISO/IEC 42001, ISO/IEC 27701), ensuring continuous regulatory compliance across global operations.
- Scalable and Flexible Infrastructure:
- Leveraging modern containerized deployment models, microservices architecture, and Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) approaches, providing unparalleled scalability, resilience, and adaptability to future technological advancements and threats.
- Enhanced Visibility and Decision-making:
- Delivering comprehensive, contextual intelligence and analytics, empowering strategic cybersecurity decision-making and fostering continuous improvement through actionable insights.
Strategic Alignment Across Key Jurisdictions
The global landscape demands cybersecurity strategies that are adaptable and compliant with stringent, region-specific regulations. SIEMLINE’s architecture explicitly addresses these diverse standards, ensuring effective compliance and interoperability across major regions:
- Australia:
- Fully integrates with the Australian Cyber Security Centre’s (ACSC) Essential Eight, Information Security Manual (ISM), Protective Security Policy Framework (PSPF), and Privacy Act 1988, enabling streamlined governance for Australian enterprises and government agencies.
- United States:
- Comprehensive alignment with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), NIST SP 800-series guidelines (including Zero Trust frameworks), Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), FISMA, HIPAA, and other critical U.S. cybersecurity regulations, ensuring rigorous compliance for federal, state, and private sector entities.
- Europe:
- Facilitates seamless compliance with stringent European regulatory standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2), ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27701, and the forthcoming European Union AI Act, positioning organizations confidently within the demanding European regulatory environment.
7.2 Commitment to Continuous Improvement
Central to the SIEMLINE framework is the principle of continuous improvement. Leveraging industry-standard methodologies such as the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, SIEMLINE ensures sustained effectiveness, agility, and adaptability. Organizations adopting SIEMLINE will benefit from iterative refinement processes, ongoing performance evaluations, and continuous alignment with emerging threats, technologies, and regulatory requirements.
7.3 Strategic Vision and Future Direction
Looking forward, SIEMLINE serves as a strategic enabler, facilitating organizations’ transformation towards intelligent cybersecurity operations. Future enhancements will include:
- Continuous Enhancement of AI Capabilities:
- Increasing predictive and behavioral analytics sophistication to anticipate evolving threats proactively and reduce vulnerability windows.
- Broader Ecosystem Integration:
- Expanding interoperability and integration capabilities with emerging cybersecurity technologies and platforms, continuously supporting the flexibility of the cybersecurity ecosystem.
- Innovation through Collaboration:
- Encouraging global collaboration among cybersecurity practitioners, regulatory bodies, academic institutions, and private sector innovators, fostering shared best practices and collective defense.
7.4 Call to Action
Organizations committed to maintaining resilience and leadership in cybersecurity are encouraged to adopt SIEMLINE as their core framework, embedding intelligence-driven security practices, proactive threat management, and robust compliance frameworks into their operational fabric. SIEMLINE provides organizations with a clear roadmap for enhanced security posture, compliance assurance, and operational excellence, ultimately delivering significant strategic and operational advantages in a rapidly evolving global cybersecurity landscape.
7.5 Final Remarks
In conclusion, the adoption and implementation of the SIEMLINE architecture represent a foundational step in achieving a sophisticated cybersecurity posture. It positions organizations to confidently address modern cybersecurity challenges, streamline compliance management, and foster strategic cybersecurity decision-making. SIEMLINE is not merely a technical solution; it is a strategic imperative that empowers organizations to safeguard their digital future, maintain stakeholder trust, and achieve sustainable cybersecurity resilience in a continuously evolving global threat landscape.